When a company has negative owner’s equity and the owner takes draws from the company, those draws may be taxable as capital gains on the owner’s tax return. For that reason, business owners should monitor their capital accounts and try not to take money from the company unless their capital account has a positive balance. In the case of acquisition, it is the value of company sales minus any liabilities owed by the company not transferred with the sale.

Accounting Equation Formula and Calculation
- You might own a 70% stake in the company while your partner owns 30%, for example.
- The investor records their share of the investee’s earnings as revenue from investment on the income statement.
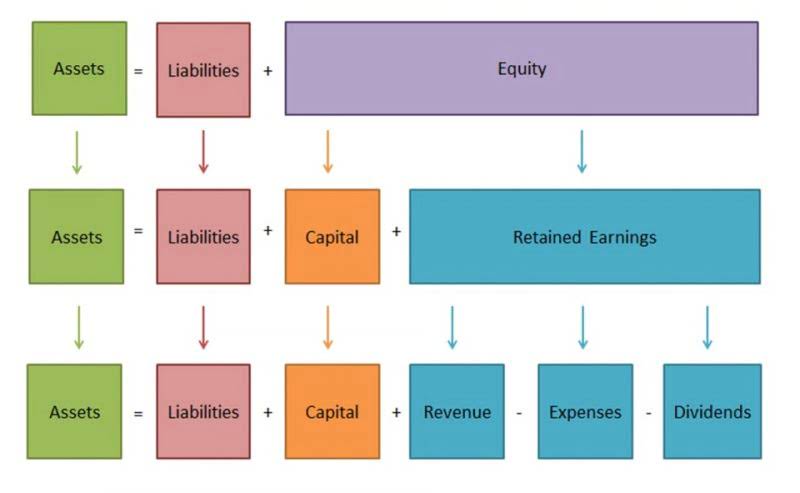
- The fundamental accounting equation, as mentioned earlier, states that total assets are equal to the sum of the total liabilities and total shareholders equity.
- If negative, the company’s liabilities exceed its assets; if prolonged, this is considered balance sheet insolvency.
Significant influence is defined as an ability to exert power over another company. This power includes representation on the board of directors, involvement in policy development, and the interchanging of managerial personnel. The required reserve ratio is the percentage of deposits that banks are required to hold as reserves. In this scenario, the required reserve ratio is 10%, and the bank has $1 million in reserves and $10 million in deposits. When customers deposit an additional $100,000, the total deposits increase to $10.1 million.
Example: How to Calculate the Accounting Equation from Transactions
If you understand equity, you’ll feel confident bringing in outside investors, working with business partners, and understanding how much your “share” of the business is actually worth. Shares are small pieces of your company that are worth a certain dollar value. If you total up the value of all the shares you own, that’s your total stock in the company. Treasury stocks are repurchased shares of the company that are held for potential resale to investors. It is the difference between shares offered for subscription and outstanding shares of a company. Through years of advertising and the development of a customer base, a company’s brand can come to have an inherent value.
Is Stockholders’ Equity Equal to Cash on Hand?
- A final type of private equity is a Private Investment in a Public Company (PIPE).
- If this figure is negative, it may indicate an oncoming bankruptcy for that business, particularly if there exists a large debt liability as well.
- Introduced species can have a significant impact on native species, particularly when it comes to competition for resources and predation.
- Conceptually, stockholders’ equity is useful as a means of judging the funds retained within a business.
- Upon calculating the total assets and liabilities, company or shareholders’ equity can be determined.
At the end of year one, XYZ Corp. reports a net income of $50,000 and pays $10,000 in dividends to its shareholders. At the time of purchase, ABC Co. records a debit of $200,000 to “Investment in XYZ Corp.” (an asset account) and a credit in the same amount to cash. It typically includes information such as financial statements, annual reports, recent press releases, and industry reports. The purpose of a PIB is to provide transparency and information to investors, analysts, and other interested parties. Equity research reports, on the other hand, are typically produced by financial analysts or investment banks and are used to provide investment recommendations to their clients. While equity research reports may contain valuable information about a company, they are not typically included in a PIB as they are not produced or endorsed by the company itself.


The house has a current market value of $175,000, and the mortgage owed totals $100,000. Sam has $75,000 worth of equity in the home or $175,000 (asset total) – $100,000 (liability total). Home equity is roughly comparable to the value contained in homeownership. The amount of equity one has in their residence represents how much of the home they own outright by subtracting from the mortgage debt owed.
Accounting Equation Formula
- Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction carried out by a company, the accounting system is referred to as double-entry accounting.
- Return on equity is a measure that analysts use to determine how effectively a company uses equity to generate a profit.
- You only enter the transactions once rather than show the impact of the transactions on two or more accounts.
- Stock is part of a business’s equity in accounting, but equity includes more than just stock.
- In this case, you purchased a put option on ABC common stock for $3 per contract, and the exercise price is $50.
- But armed with this essential info, you’ll be able to make big purchases confidently, and know exactly where your business stands.
The value of $60.2 billion in shareholders’ equity represents the amount left for stockholders if Apple liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities. Treasury shares continue to count as issued shares, but they are not considered to be outstanding and are thus not included equity equation accounting in dividends or the calculation of earnings per share (EPS). Treasury shares can always be reissued back to stockholders for purchase when companies need to raise more capital. If a company doesn’t wish to hang on to the shares for future financing, it can choose to retire the shares.

Order To Cash
- Finance professionals are typically concerned with forecasting or estimating how a company will perform in the future.
- When your company incorporates, it has to call a board meeting to decide how many shares each of the company’s original owners will get.
- Cash flows or the assets of the company being acquired usually secure the loan.
- Return on equity (ROE) is a measure of financial performance calculated by dividing net income by shareholder equity.
- Like the accounting equation, it shows that a company’s total amount of assets equals the total amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity.
- Each example shows how different transactions affect the accounting equations.
If a business buys raw materials and pays in cash, it will result in an increase in the company’s inventory (an asset) while reducing cash capital (another asset). Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction carried out by a company, the accounting system is referred to as double-entry accounting. Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital (assets) to all sources of capital, where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity. If you look at the balance sheet, you can see that the total owner’s equity is $95,000.
